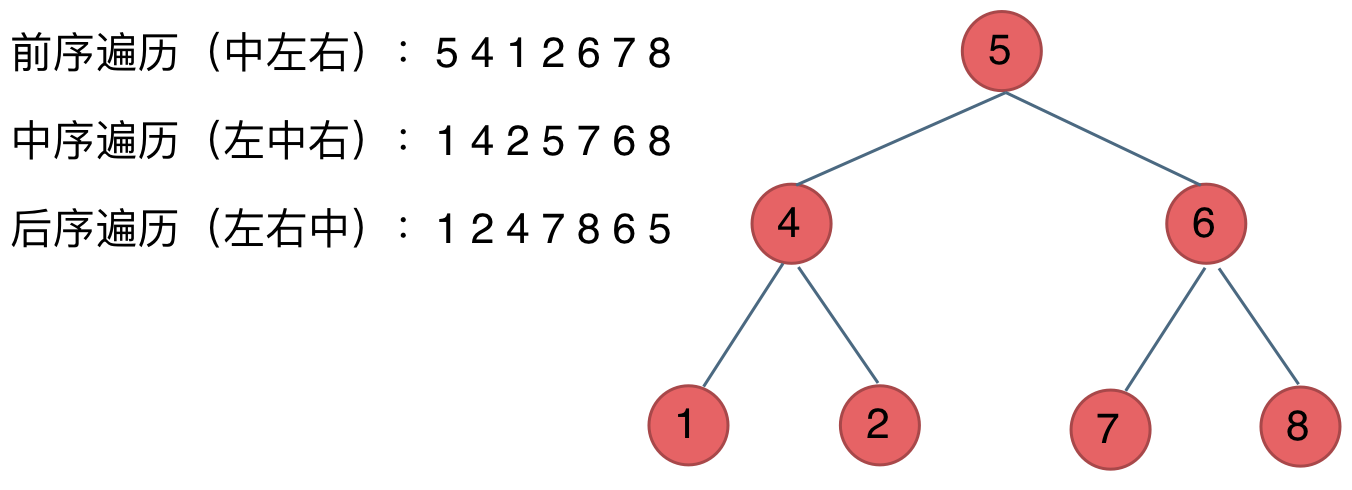
二叉树的递归遍历
看如下中间节点的顺序,就可以发现,中间节点的顺序就是所谓的遍历方式
- 前序遍历:中左右
- 中序遍历:左中右
- 后序遍历:左右中
大家可以对着如下图,看看自己理解的前后中序有没有问题。
二叉树的定义
刚刚我们说过了二叉树有两种存储方式顺序存储,和链式存储,顺序存储就是用数组来存,这个定义没啥可说的,我们来看看链式存储的二叉树节点的定义方式。
C++代码如下:
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
二叉树的递归遍历
前序遍历:
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& vec) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
vec.push_back(cur->val); // 中
traversal(cur->left, vec); // 左
traversal(cur->right, vec); // 右
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
traversal(root, result);
return result;
}
};
那么前序遍历写出来之后,中序和后序遍历就不难理解了,代码如下:
中序遍历:
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& vec) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
traversal(cur->left, vec); // 左
vec.push_back(cur->val); // 中
traversal(cur->right, vec); // 右
}
后序遍历:
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& vec) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
traversal(cur->left, vec); // 左
traversal(cur->right, vec); // 右
vec.push_back(cur->val); // 中
}
二叉树的迭代遍历
前序遍历(迭代法)
我们先看一下前序遍历。
前序遍历是中左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将根节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。
为什么要先加入 右孩子,再加入左孩子呢? 因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
动画如下:

不难写出如下代码: (注意代码中空节点不入栈)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
}
return result;
}
};
中序遍历(迭代法)
那么在使用迭代法写中序遍历,就需要借用指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素。
动画如下:

中序遍历,可以写出如下代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top(); // 从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据)
st.pop();
result.push_back(cur->val); // 中
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
};
后序遍历(迭代法)
再来看后序遍历,先序遍历是中左右,后续遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了,如下图:

所以后序遍历只需要前序遍历的代码稍作修改就可以了,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 相对于前序遍历,这更改一下入栈顺序 (空节点不入栈)
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 空节点不入栈
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 将结果反转之后就是左右中的顺序了
return result;
}
};
因为前序遍历中访问节点(遍历节点)和处理节点(将元素放进result数组中)可以同步处理,但是中序就无法做到同步!
二叉树的统一迭代法
迭代法中序遍历
中序遍历代码如下:(详细注释)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop(); // 将该节点弹出,避免重复操作,下面再将右中左节点添加到栈中
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 添加右节点(空节点不入栈)
st.push(node); // 添加中节点
st.push(NULL); // 中节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点做为标记。
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 添加左节点(空节点不入栈)
} else { // 只有遇到空节点的时候,才将下一个节点放进结果集
st.pop(); // 将空节点弹出
node = st.top(); // 重新取出栈中元素
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val); // 加入到结果集
}
}
return result;
}
};
看代码有点抽象我们来看一下动画(中序遍历):

动画中,result数组就是最终结果集。
迭代法前序遍历
迭代法前序遍历代码如下: (注意此时我们和中序遍历相比仅仅改变了两行代码的顺序)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return result;
}
};
#迭代法后序遍历
后续遍历代码如下: (注意此时我们和中序遍历相比仅仅改变了两行代码的顺序)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return result;
}
};
二叉树层序遍历
102.二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。

使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下:

这样就实现了层序从左到右遍历二叉树。
代码如下:这份代码也可以作为二叉树层序遍历的模板,打十个就靠它了。
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
// 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(vec);
}
return result;
}
};
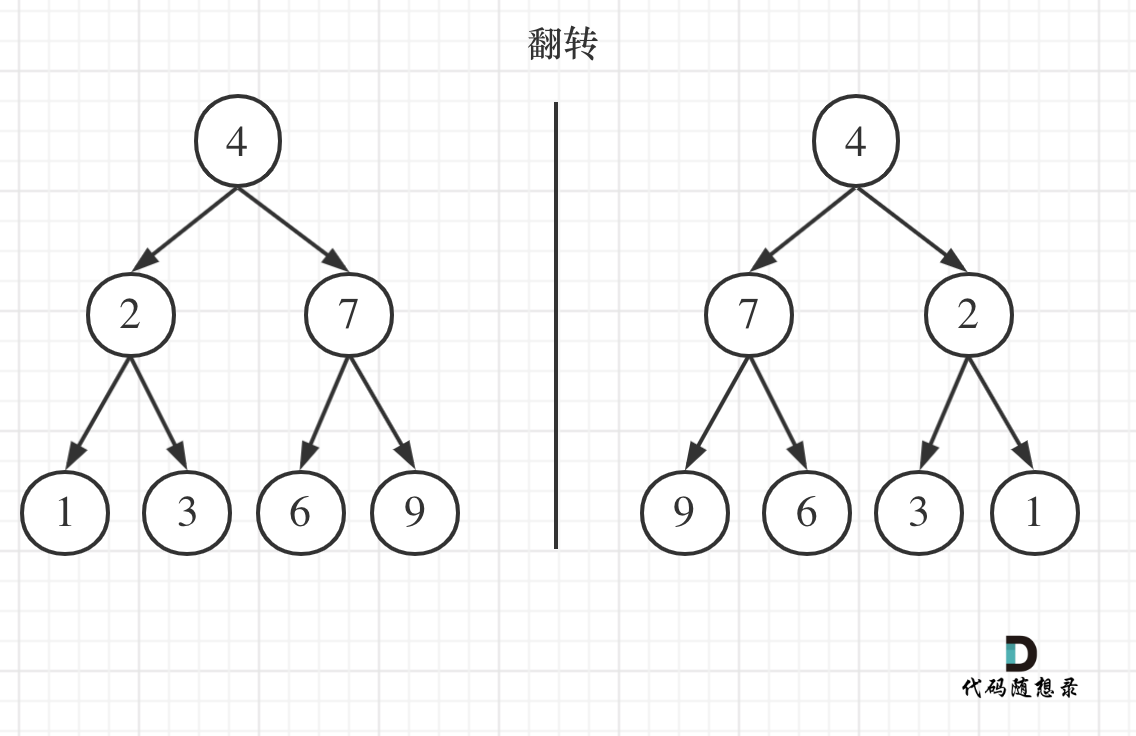
226.翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。

如果要从整个树来看,翻转还真的挺复杂,整个树以中间分割线进行翻转,如图:
递归法
对于二叉树的递归法的前中后序遍历,已经在**二叉树:前中后序递归遍历 (opens new window)**详细讲解了。
我们下文以前序遍历为例,通过动画来看一下翻转的过程:

基于这递归三步法,代码基本写完,C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 左
invertTree(root->right); // 右
return root;
}
};
迭代法
深度优先遍历
**二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做! (opens new window)**中给出了前中后序迭代方式的写法,所以本地可以很轻松的切出如下迭代法的代码:
C++代码迭代法(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if(node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if(node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
}
return root;
}
};
如果这个代码看不懂的话可以在回顾一下**二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做! (opens new window)**。
我们在**二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的统一写法 (opens new window)**中介绍了统一的写法,所以,本题也只需将文中的代码少做修改便可。
C++代码如下迭代法(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理逻辑
}
}
return root;
}
};
1234567891011121314151617181920212223
如果上面这个代码看不懂,回顾一下文章**二叉树:前中后序迭代方式的统一写法 (opens new window)**。
广度优先遍历
也就是层序遍历,层数遍历也是可以翻转这棵树的,因为层序遍历也可以把每个节点的左右孩子都翻转一遍,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
123456789101112131415161718
如果对以上代码不理解,或者不清楚二叉树的层序遍历,可以看这篇**二叉树:层序遍历登场!(opens new window**
拓展
文中我指的是递归的中序遍历是不行的,因为使用递归的中序遍历,某些节点的左右孩子会翻转两次。
如果非要使用递归中序的方式写,也可以,如下代码就可以避免节点左右孩子翻转两次的情况:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
invertTree(root->left); // 左
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 注意 这里依然要遍历左孩子,因为中间节点已经翻转了
return root;
}
};
代码虽然可以,但这毕竟不是真正的递归中序遍历了。
但使用迭代方式统一写法的中序是可以的。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理逻辑
}
}
return root;
}
};
为什么这个中序就是可以的呢,因为这是用栈来遍历,而不是靠指针来遍历,避免了递归法中翻转了两次的情况,大家可以画图理解一下,这里有点意思的
101. 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。

比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。如图所示:

因为要遍历两棵树而且要比较内侧和外侧节点,所以准确的来说是一个树的遍历顺序是左右中,一个树的遍历顺序是右左中。
节点为空的情况有:(注意我们比较的其实不是左孩子和右孩子,所以如下我称之为左节点右节点)
- 左节点为空,右节点不为空,不对称,return false
- 左不为空,右为空,不对称 return false
- 左右都为空,对称,返回true
递归法
最后递归的C++整体代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
// 首先排除空节点的情况
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
// 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
// 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况
// 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); // 左子树:左、 右子树:右
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); // 左子树:右、 右子树:左
bool isSame = outside && inside; // 左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理)
return isSame;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};
当然我可以把如上代码整理如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
else return compare(left->left, right->right) && compare(left->right, right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};




