代码随想录算法总结(C++)版本——栈和队列
代码随想录算法总结(C++)版本——栈和队列
Created: September 2, 2022 1:06 PM
232.用栈实现队列
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。empty() -- 返回队列是否为空。
示例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.peek(); // 返回 1
queue.pop(); // 返回 1
queue.empty(); // 返回 false
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 -- 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
- 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)。
C++代码如下:
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
// 只有当stOut为空的时候,再从stIn里导入数据(导入stIn全部数据)
if (stOut.empty()) {
// 从stIn导入数据直到stIn为空
while(!stIn.empty()) {
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
}
int result = stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
int res = this->pop(); // 直接使用已有的pop函数
stOut.push(res); // 因为pop函数弹出了元素res,所以再添加回去
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();
}
};
225. 用队列实现栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
模拟的队列执行语句如下:
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.pop(); // 注意弹出的操作
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
queue.pop(); // 注意弹出的操作
queue.pop();
queue.pop();
queue.empty();

详细如代码注释所示:
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que1;
queue<int> que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que1.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将que1 导入que2,但要留下最后一个元素
que2.push(que1.front());
que1.pop();
}
int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要返回的值
que1.pop();
que1 = que2; // 再将que2赋值给que1
while (!que2.empty()) { // 清空que2
que2.pop();
}
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que1.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que1.empty();
}
};
优化
其实这道题目就是用一个队列就够了。
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时在去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
C++优化代码
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了
que.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
- 输入: "()"
- 输出: true
示例 2:
- 输入: "()[]{}"
- 输出: true
示例 3:
- 输入: "(]"
- 输出: false
先来分析一下 这里有三种不匹配的情况,
- 第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了 ,所以不匹配。
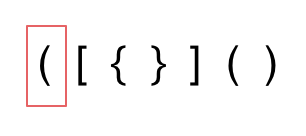
- 第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上。
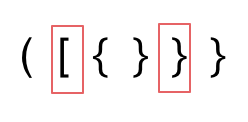
- 第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
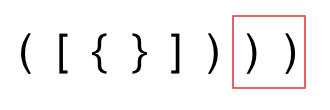
我们的代码只要覆盖了这三种不匹配的情况,就不会出问题,可以看出 动手之前分析好题目的重要性。
动画如下:

实现C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');
else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');
else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']');
// 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false
// 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有我们要匹配的字符。所以return false
else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false;
else st.pop(); // st.top() 与 s[i]相等,栈弹出元素
}
// 第一种情况:此时我们已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false,否则就return true
return st.empty();
}
};
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。
在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。
在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。
示例:
- 输入:"abbaca"
- 输出:"ca"
- 解释:例如,在 "abbaca" 中,我们可以删除 "bb" 由于两字母相邻且相同,这是此时唯一可以执行删除操作的重复项。之后我们得到字符串 "aaca",其中又只有 "aa" 可以执行重复项删除操作,所以最后的字符串为 "ca"。
提示:
- 1 <= S.length <= 20000
- S 仅由小写英文字母组成。
如动画所示:

从栈中弹出剩余元素,此时是字符串ac,因为从栈里弹出的元素是倒序的,所以在对字符串进行反转一下,就得到了最终的结果。
C++代码 :
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
stack<char> st;
for (char s : S) {
if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {
st.push(s);
} else {
st.pop(); // s 与 st.top()相等的情况
}
}
string result = "";
while (!st.empty()) { // 将栈中元素放到result字符串汇总
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
reverse (result.begin(), result.end()); // 此时字符串需要反转一下
return result;
}
};
123456789101112131415161718192021
当然可以拿字符串直接作为栈,这样省去了栈还要转为字符串的操作。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
string result;
for(char s : S) {
if(result.empty() || result.back() != s) {
result.push_back(s);
}
else {
result.pop_back();
}
}
return result;
}
};
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的运算符包括 + , - , * , / 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
说明:
整数除法只保留整数部分。 给定逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
- 输入: ["2", "1", "+", "3", " * "]
- 输出: 9
- 解释: 该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
示例 2:
输入: ["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", " * ", "/", " * ", "17", "+", "5", "+"]
输出: 22
解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5 = (0 + 17) + 5 = 17 + 5 = 22在进一步看,本题中每一个子表达式要得出一个结果,然后拿这个结果再进行运算,那么这岂不就是一个相邻字符串消除的过程,和1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 (opens new window)中的对对碰游戏是不是就非常像了。
如动画所示:

https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/gifs/150.逆波兰表达式求值.gif 相信看完动画大家应该知道,这和**1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 (opens new window)**是差不错的,只不过本题不要相邻元素做消除了,而是做运算!
C++代码如下:
class Solution { public: int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) { stack<int> st; for (int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++) { if (tokens[i] == "+" || tokens[i] == "-" || tokens[i] == "*" || tokens[i] == "/") { int num1 = st.top(); st.pop(); int num2 = st.top(); st.pop(); if (tokens[i] == "+") st.push(num2 + num1); if (tokens[i] == "-") st.push(num2 - num1); if (tokens[i] == "*") st.push(num2 * num1); if (tokens[i] == "/") st.push(num2 / num1); } else { st.push(stoi(tokens[i])); } } int result = st.top(); st.pop(); // 把栈里最后一个元素弹出(其实不弹出也没事) return result; } };239. 滑动窗口最大值
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
来看一下单调队列如何维护队列里的元素。
动画如下:

设计单调队列的时候,pop,和push操作要保持如下规则:
- pop(value):如果窗口移除的元素value等于单调队列的出口元素,那么队列弹出元素,否则不用任何操作
- push(value):如果push的元素value大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列入口的元素弹出,直到push元素的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止
保持如上规则,每次窗口移动的时候,只要问que.front()就可以返回当前窗口的最大值。
为了更直观的感受到单调队列的工作过程,以题目示例为例,输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,动画如下:

C++代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
class MyQueue { //单调队列(从大到小)
public:
deque<int> que; // 使用deque来实现单调队列
// 每次弹出的时候,比较当前要弹出的数值是否等于队列出口元素的数值,如果相等则弹出。
// 同时pop之前判断队列当前是否为空。
void pop(int value) {
if (!que.empty() && value == que.front()) {
que.pop_front();
}
}
// 如果push的数值大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列后端的数值弹出,直到push的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止。
// 这样就保持了队列里的数值是单调从大到小的了。
void push(int value) {
while (!que.empty() && value > que.back()) {
que.pop_back();
}
que.push_back(value);
}
// 查询当前队列里的最大值 直接返回队列前端也就是front就可以了。
int front() {
return que.front();
}
};
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
MyQueue que;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { // 先将前k的元素放进队列
que.push(nums[i]);
}
result.push_back(que.front()); // result 记录前k的元素的最大值
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) {
que.pop(nums[i - k]); // 滑动窗口移除最前面元素
que.push(nums[i]); // 滑动窗口前加入最后面的元素
result.push_back(que.front()); // 记录对应的最大值
}
return result;
}
};
347.前 K 个高频元素
给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。
示例 1:
- 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
- 输出: [1,2]
示例 2:
- 输入: nums = [1], k = 1
- 输出: [1]
提示:
- 你可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。
- 你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 $O(n \log n)$ , n 是数组的大小。
- 题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前 k 个高频元素的集合是唯一的。
- 你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
这道题目主要涉及到如下三块内容:
- 要统计元素出现频率
- 对频率排序
- 找出前K个高频元素
寻找前k个最大元素流程如图所示:(图中的频率只有三个,所以正好构成一个大小为3的小顶堆,如果频率更多一些,则用这个小顶堆进行扫描)

我们来看一下C++代码:
// 时间复杂度:O(nlogk)
// 空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
// 小顶堆
class mycomparison {
public:
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& lhs, const pair<int, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.second > rhs.second;
}
};
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// 要统计元素出现频率
unordered_map<int, int> map; // map<nums[i],对应出现的次数>
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
map[nums[i]]++;
}
// 对频率排序
// 定义一个小顶堆,大小为k
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, mycomparison> pri_que;
// 用固定大小为k的小顶堆,扫面所有频率的数值
for (unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++) {
pri_que.push(*it);
if (pri_que.size() > k) { // 如果堆的大小大于了K,则队列弹出,保证堆的大小一直为k
pri_que.pop();
}
}
// 找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒序来输出到数组
vector<int> result(k);
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] = pri_que.top().first;
pri_que.pop();
}
return result;
}
};




