HJ76 尼科彻斯定理
HJ76 尼科彻斯定理
描述
验证尼科彻斯定理,即:任何一个整数m的立方都可以写成m个连续奇数之和。
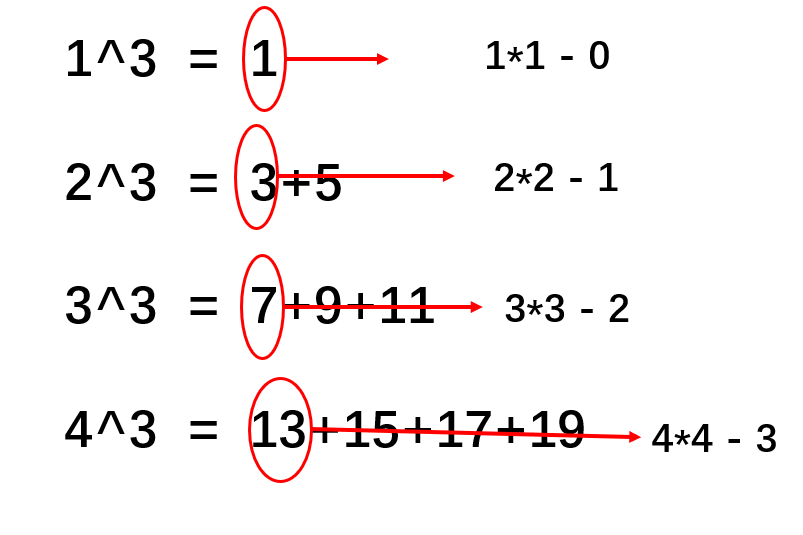
例如:
1^3=1
2^3=3+5
3^3=7+9+11
4^3=13+15+17+19
输入一个正整数m(m≤100),将m的立方写成m个连续奇数之和的形式输出。
数据范围:1≤m≤100
进阶:时间复杂度:O(m) ,空间复杂度:O(1)
输入描述:
输入一个int整数
输出描述:
输出分解后的string
方法一:遍历查找
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m;
while(cin >> m){
int pow = m * m * m; //先获取三次方的值
for(int i = 1; i < pow; i += 2){ //从1开始找到pow
if(m * i + m * (m - 1) == pow){ //比较等差数列和与三次幂是否相等
cout << i; //相等开始输出连续m个数字
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++)
cout << '+' << i + 2 * j;
cout << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
方法二:数学规律
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m;
while(cin >> m){
int odd = m * m - (m - 1); //根据公式获取起点奇数
cout << odd;
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) //遍历后续m-1个奇数
cout << '+' << odd + 2 * i; //输出
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ77 火车进站
描述
给定一个正整数N代表火车数量,0<N<10,接下来输入火车入站的序列,一共N辆火车,每辆火车以数字1-9编号,火车站只有一个方向进出,同时停靠在火车站的列车中,只有后进站的出站了,先进站的才能出站。
要求输出所有火车出站的方案,以字典序排序输出。
数据范围:1≤n≤10
进阶:时间复杂度:O(n!) ,空间复杂度:O(n)
输入描述:
第一行输入一个正整数N(0 < N <= 10),第二行包括N个正整数,范围为1到10。
输出描述:
输出以字典序从小到大排序的火车出站序列号,每个编号以空格隔开,每个输出序列换行,具体见sample。
方法一:全排列+栈


#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool check(vector<int>& order, vector<int>& out){ //根据进来的顺序检查有无这种出去的顺序
stack<int> s;
int j = 0; //out数组的下标
for(int i = 0; i < order.size(); i++){
s.push(order[i]); //每次火车入栈
while(!s.empty() && s.top() == out[j]){ //如果刚好栈顶等于输出,就全部出栈
s.pop();
j++;
}
}
return s.empty();
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
vector<vector<int> > output;
vector<int> nums(n); //记录所有的数字
vector<int> order(n); //记录数字进来的顺序
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> nums[i];
order[i] = nums[i];
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); //对数字按照字典序排序
do{
output.push_back(nums);
}while(next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())); //获取全排列
for(int i = 0; i < output.size(); i++){
if(check(order, output[i])){ //检查每一种排列输出的可能性
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
cout << output[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
方法二:dfs+回溯
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, stack<int> s, vector<int> temp, set<vector<int>>& output, int index, int& n){
if(temp.size() == n){ //该情况结果已经完成
output.insert(temp);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){ //每次两个操作
if(i == 0 && !s.empty()){ //要么从栈出弹出一个输出
int num = s.top();
s.pop();
temp.push_back(num);
dfs(nums, s, temp, output, index, n); //继续递归
s.push(num); //回溯
temp.pop_back();
}else if(i == 1 && index < n){ //要么从数组中拿出一个加入栈中
int num = nums[index];
s.push(num);
index++;
dfs(nums, s, temp, output, index, n); //继续递归
index--; //回溯
s.pop();
}
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
vector<int> nums(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> nums[i];
set<vector<int> > output;
stack<int> s;
vector<int> temp; //记录某一种情况的输出结果
s.push(nums[0]); // 默认第一辆车都要先进去
dfs(nums, s, temp, output, 1, n); //dfs找到全排列
for(auto iter = output.begin(); iter != output.end(); iter++){ //遍历集合
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) //输出集合中每一个数组
cout << (*iter)[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
HJ80 整型数组合并
描述
题目标题:
将两个整型数组按照升序合并,并且过滤掉重复数组元素。
输出时相邻两数之间没有空格。
输入描述:
输入说明,按下列顺序输入:
1 输入第一个数组的个数
2 输入第一个数组的数值
3 输入第二个数组的个数
4 输入第二个数组的数值
输出描述:
输出合并之后的数组
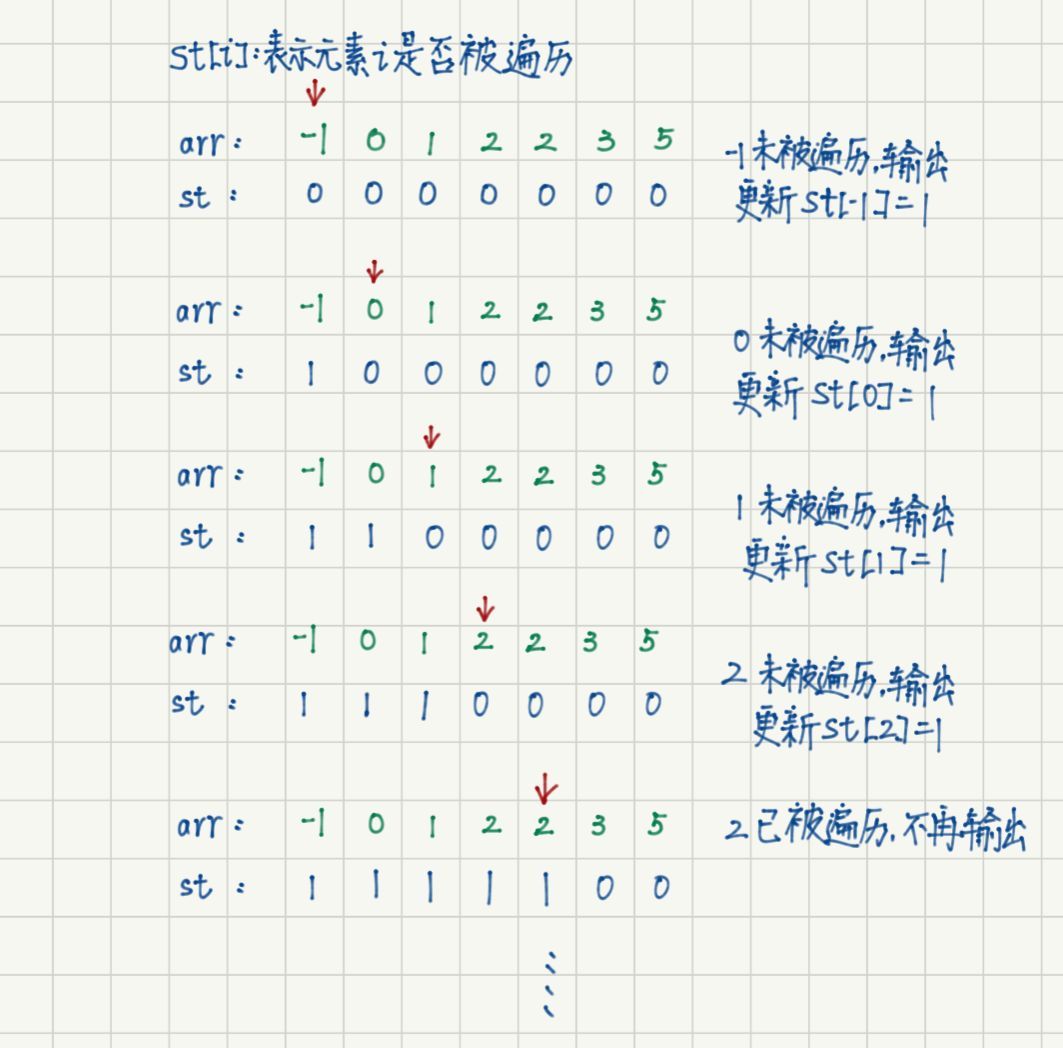
方法一:hash + 排序
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> arr;
int n, m;
int main() {
while (cin >> n) { //多组测试数据
arr.clear();
//输入与合并两个数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
arr.push_back(x);
}
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
arr.push_back(x);
}
//对合并数组升序排序
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
map<int, int> st;
vector<int> ans;
//遍历并保存未标记元素
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i ++ ) {
if (!st[arr[i]]) {
st[arr[i]] = 1; //更新标记
ans.push_back(arr[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i ++ ) cout << ans[i];
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
方法二:直接使用stl函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> arr;
int n, m;
int main() {
while (cin >> n) { //多组测试数据
arr.clear();
//输入与合并两个数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
arr.push_back(x);
}
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
arr.push_back(x);
}
//对合并数组升序排序
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
//去重
arr.erase(unique(arr.begin(), arr.end()), arr.end());
for (auto i : arr) cout << i;
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
HJ81 字符串字符匹配
描述
判断短字符串S中的所有字符是否在长字符串T中全部出现。
请注意本题有多组样例输入。
数据范围:1≤len(S),len(T)≤200
进阶:时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)
输入描述:
输入两个字符串。第一个为短字符串,第二个为长字符串。两个字符串均由小写字母组成。
输出描述:
如果短字符串的所有字符均在长字符串中出现过,则输出字符串"true"。否则输出字符串"false"。
方法一: find()

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1;
string str2;
while (getline(cin, str1), getline(cin, str2))//逐行输入
{
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++)
{
if (str2.find(str1[i]) == str2.npos)//判断字符str1[i]是否在str2中出现
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag)//若有字符在str2中没有出现,则flag为false
{
cout << "true" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "false" << endl;
}
}
}
方法二:遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1;
string str2;
while (getline(cin, str1), getline(cin, str2))//逐行输入
{
vector<int> count(26,0);//统计每个字符出现的次数
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < str2.size(); i++)//遍历str2,统计每个字符出现的次数
{
count[str2[i]-'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0; i< str1.size(); i++)
{
if(count[str1[i]-'a']==0){//count为0表示str2中没有这个字符
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag)//若有字符在str2中没有出现,则flag为false
{
cout << "true" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "false" << endl;
}
}
}
HJ82 将真分数分解为埃及分数
描述
分子为1的分数称为埃及分数。现输入一个真分数(分子比分母小的分数,叫做真分数),请将该分数分解为埃及分数。如:8/11 = 1/2+1/5+1/55+1/110。
注:真分数指分子小于分母的分数,分子和分母有可能gcd不为1!
如有多个解,请输出任意一个。
输入描述:
输入一个真分数,String型
输出描述:
输出分解后的string
方法一:斐波那契分解分数
用斐波那契分解分数,步骤如下:
设某个真分数的分子为a,分母为b;
把b除以a的商部分加1后的值作为埃及分数的某一个分母c;
将a乘以c再减去b,作为新的a;
将b乘以c,得到新的b;
如果a大于1且能整除b,则最后一个分母为b/a;算法结束;
或者,如果a等于1,则最后一个分母为b;算法结束;

点击并拖拽以移动
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char ch;
int a,b;
while(cin>>a>>ch>>b){
while(a!=1){
int c=b/a+1;//第一个分解式
cout<<1<<"/"<<c<<"+";
a= a-b%a;//更新a
b=b*c;//更新b
if (b%a==0){//可以约分
b=b/a;
a=1;
}
}
cout<<a<<"/"<<b<<endl;
}
}
方法二:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void calculate(int a, int b){
if(a==1){//a为1时直接输出
cout<<1<<"/"<<b<<endl;
return;
}
if(b%a==0){
cout<<1<<"/"<<b/a<<endl;//直接约分
return;
}
cout << 1 << "/" << b / a + 1 << "+";
calculate(a - b % a, b * (b / a + 1)); //更新a和b的值,递归计算
}
int main(){
char ch;
int a,b;
while(cin>>a>>ch>>b){
calculate(a, b);
}
}
方法三:迭代
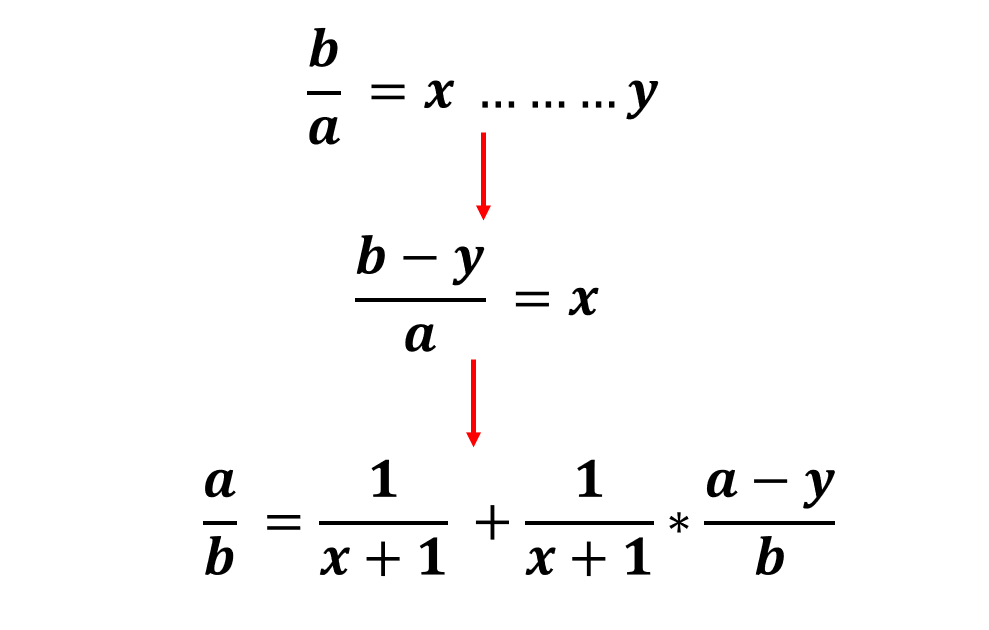
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a, b; //分别是分子分母
char op; //除号
while(cin >> a >> op >> b){
while(a != 1){ //直到最后的a为1
if(b % a == 0){ //先去掉公因子
b = b / a;
break;
}
//按照公式推算运算
int x = b / a;
int y = b % a;
cout << 1 << op << x + 1 << "+";
a -= y;
b *= x + 1;
}
cout << 1 << op << b << endl;
}
}
HJ83 二维数组操作

输入描述:
输入数据按下列顺序输入:
1 表格的行列值
2 要交换的两个单元格的行列值
3 输入要插入的行的数值
4 输入要插入的列的数值
5 输入要查询的单元格的坐标
输出描述:
输出按下列顺序输出:
1 初始化表格是否成功,若成功则返回0, 否则返回-1
2 输出交换单元格是否成功
3 输出插入行是否成功
4 输出插入列是否成功
5 输出查询单元格数据是否成功
方法一:直接判断
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m, n;
while(cin >> m >> n){ //输入矩阵的行与列
if(m > 9 || n > 9) //行列数小于等于9
cout << -1 << endl;
else
cout << 0 << endl;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2; //输入要交换位置的两个坐标
if(x1 >= 0 && x1 < m && y1 >= 0 && y1 < n && x2 >= 0 && x2 < m && y2 >= 0 && y2 < n) //坐标在数组范围内
cout << 0 << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
int x;
cin >> x; //输入插入的行
if(x >= 0 && x < m && m + 1 <= 9) //插入位置在数组范围内,且插入后不会超过9
cout << 0 << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
int y;
cin >> y; //输入插入的列
if(y >= 0 && y < n && n + 1 <= 9) //插入位置在数组范围内,且插入后不会超过9
cout << 0 << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
cin >> x >> y; //输入要查找的位置
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) //在数组范围内
cout << 0 << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:类
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class matrix{
private:
int m, n; //二维数组的行列
vector<vector<int>> arr; //二维数组的元素
public:
int init(int m, int n){ //输入m和n,初始化m*n大小的表格。
if(m > 9 || n > 9) //行列数小于等于9
return -1;
this->m = m;
this->n = n;
arr.resize(m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
arr[i].resize(n);
return 0;
}
int swap_two(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2){
if(x1 >= 0 && x1 < m && y1 >= 0 && y1 < n && x2 >= 0 && x2 < m && y2 >= 0 && y2 < n){ //坐标在数组范围内
swap(arr[x1][y1], arr[x2][y2]);
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
int insert_row(int x){ //输入x,在第x行左边添加一行
if(x < 0 || x > m - 1 || m + 1 > 9) //插入位置在数组范围内,且插入后不会超过9
return -1;
return 0;
}
int insert_col(int y){ //输入y,在第y行上方添加一列
if(y < 0 || y > n - 1 || n + 1 > 9) //插入位置在数组范围内,且插入后不会超过9
return -1;
return 0;
}
int find(int x, int y){ //查找x,y
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n)
return 0;
return -1;
}
};
int main(){
matrix mat;
int m, n, x1, y1, x2, y2, x, y, find_x, find_y;
while(cin >> m >> n >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> x >> y >> find_x >> find_y){
cout << mat.init(m, n) << endl;
cout << mat.swap_two(x1, y1, x2, y2) << endl;
cout << mat.insert_row(x) << endl;
cout << mat.insert_col(y) << endl;
cout << mat.find(find_x, find_y) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ84 统计大写字母个数
描述
找出给定字符串中大写字符(即'A'-'Z')的个数。
数据范围:字符串长度:1≤∣s∣≤250
字符串中可能包含空格或其他字符
进阶:时间复杂度:O(n) ,空间复杂度:O(n)
输入描述:
对于每组样例,输入一行,代表待统计的字符串
输出描述:
输出一个整数,代表字符串中大写字母的个数
方法一:ASCⅡ码比较

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) //遍历字符串每个字符
if(s[i] >= 65 && s[i] <= 90) //用ASCⅡ码比较
count++;
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:库函数
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) //遍历字符串每个字符
if(isupper(s[i])) //用函数检查是否是大写字母
count++;
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ85 最长回文子串
描述
给定一个仅包含小写字母的字符串,求它的最长回文子串的长度。
所谓回文串,指左右对称的字符串。
所谓子串,指一个字符串删掉其部分前缀和后缀(也可以不删)的字符串
数据范围:字符串长度1≤s≤350
进阶:时间复杂度:O(n) ,空间复杂度:O(n)
输入描述:
输入一个仅包含小写字母的字符串
输出描述:
返回最长回文子串的长度
方法一:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string instr;
cin >> instr;
int strlen = instr.length();
// cout << "len=" << strlen << endl;
int maxHuiwenLen = 1; // 最大回文子串长度
string maxHuiwenStr = instr.substr(0,1);
int firstIndex = 0; // 子字符串首字母在主串下标
int endIndex = 0; // 子字符串尾字母在主串下标
for (int firstIndex = 0; firstIndex < strlen; firstIndex++) { // 从第一个字符开始
int havelen = strlen - firstIndex; // 剩下的字符串长度
if (havelen < maxHuiwenLen) { // 如果剩下的字符串长度都 小于 已知的回文字符串长度就退出
break;
}
// 开始搜索回文字符串
for (endIndex = (strlen - 1); endIndex > firstIndex; endIndex--) { //从倒数一个字符开始
havelen = endIndex - firstIndex + 1; // 剩下的字符串长度
if (havelen < maxHuiwenLen) { // 如果剩下的字符串长度都 小于 已知的回文字符串长度就退出
break;
}
int offIndex = 0; // 子字符串下标
int midIndex = havelen/2;
for (offIndex = 0; offIndex < midIndex; offIndex++) {
int aIndex = firstIndex + offIndex;
int zIndex = endIndex - offIndex;
if (instr[aIndex] != instr[zIndex]) { //两端字符比较 如果不等就不是回文字符串
break;
}
}
if (offIndex == midIndex) { // 说明找到了回文字符串
maxHuiwenLen = max(maxHuiwenLen, havelen);
maxHuiwenStr = instr.substr(firstIndex, havelen);
// cout << maxHuiwenStr << endl;
}
}
}
cout << maxHuiwenLen << endl;
return 0;
}
方法二:暴力法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool check(string s, int l, int r) {
for (; l < r; l++, r--)
if (s[l] != s[r]) return false;
return true;
// 这里我们判断一个字符串是不是回文串
}
signed main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
int maxx = INT_MIN;
// 这个maxx是我们的最长回文子串的一个长度
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
// 我们第一层循环枚举的是我们这个字符串的一个起点的位置
for (int j = i; j < s.size(); j++) {
// 我们的第二层循环是用来循环我们的结尾的位置是在哪里的
if (check(s, i, j)) {
maxx = max(maxx, j - i + 1);
// 如果我们当前的这个字符串是回文串,我们更新一下最大的长度
}
}
}
cout << maxx << "\n";
return 0;
}
解法二:Manacher算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string init(string &s) {
string res = "";
res += "$#";
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) res += s[i], res += '#';
res += '^';
return res;
// 这个是在开始和结束加上通配符, 然后我们中间每个分割的地方加上#
}
void manacher(vector<int> &p, string &s) {
int mr = 0, mid;
// mr代表以mid为中心的最长回文的有边界
// mid为i和j的中心点, i以mid为对称点翻折到j的位置
for (int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (i < mr)
p[i] = min(p[mid * 2 - i], mr - i);
// 2 * mid - i为i关于mid的对称点
else
p[i] = 1;
// 超过边界总共就不是回文了
while (s[i - p[i]] == s[i + p[i]]) p[i]++;
// 不需要判断边界, 因为我们有通配符
if (i + p[i] > mr) {
mr = i + p[i];
mid = i;
}
// 我们每走一步i, 都要和mx比较, 我们希望mx尽可能的远
}
}
signed main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
s = init(s);
vector<int> p(s.size());
manacher(p, s);
// 初始化字符串和求取出来我们的每一个位置的最长长度
int maxx = INT_MIN;
for (auto &it : p) maxx = max(maxx, it);
cout << maxx - 1 << "\n";
return 0;
}
HJ86 求最大连续bit数
描述
求一个int类型数字对应的二进制数字中1的最大连续数,例如3的二进制为00000011,最大连续2个1
数据范围:数据组数:1≤t≤5 ,1\le n\le 500000\1≤n≤500000
进阶:时间复杂度:O(logn),空间复杂度:O(1)\O(1)
输入描述:
输入一个int类型数字
输出描述:
输出转成二进制之后连续1的个数
方法一:连除法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int count = 0; //记录每次统计的连续1的个数
int max_count = 0; //记录最大连续1的个数
while(n){
if(n % 2 == 1) //最后一位为1
count++;
else{ //遇到不为1
max_count = max(max_count, count); //更新最大值
count = 0; //从0开始
}
n /= 2; //去掉最后一位
}
max_count = max(max_count, count); //最后一次更新最大值
cout << max_count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:位运算

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int count = 0;
for(; n != 0; count++) //统计能够运算多少次
n &= n << 1; //与自己左移一位后比较
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ87 密码强度等级
描述
密码按如下规则进行计分,并根据不同的得分为密码进行安全等级划分。
一、密码长度:
5 分: 小于等于4 个字符
10 分: 5 到7 字符
25 分: 大于等于8 个字符
二、字母:
0 分: 没有字母
10 分: 密码里的字母全都是小(大)写字母
20 分: 密码里的字母符合”大小写混合“
三、数字:
0 分: 没有数字
10 分: 1 个数字
20 分: 大于1 个数字
四、符号:
0 分: 没有符号
10 分: 1 个符号
25 分: 大于1 个符号
五、奖励(只能选符合最多的那一种奖励):
2 分: 字母和数字
3 分: 字母、数字和符号
5 分: 大小写字母、数字和符号
最后的评分标准:
= 90: 非常安全
= 80: 安全(Secure)
= 70: 非常强
= 60: 强(Strong)
= 50: 一般(Average)
= 25: 弱(Weak)
= 0: 非常弱(Very_Weak)
对应输出为:
VERY_SECURE
SECURE
VERY_STRONG
STRONG
AVERAGE
WEAK
VERY_WEAK
请根据输入的密码字符串,进行安全评定。
注:
字母:a-z, A-Z
数字:0-9
符号包含如下: (ASCII码表可以在UltraEdit的菜单view->ASCII Table查看)
!"#$%&'()*+,-./ (ASCII码:0x21~0x2F)
:;<=>?@ (ASCII码:0x3A~0x40)
[]^_` (ASCII码:0x5B~0x60)
{|}~ (ASCII码:0x7B~0x7E)
提示:
1 <= 字符串的长度<= 300
输入描述:
输入一个string的密码
输出描述:
输出密码等级
方法一:遍历法
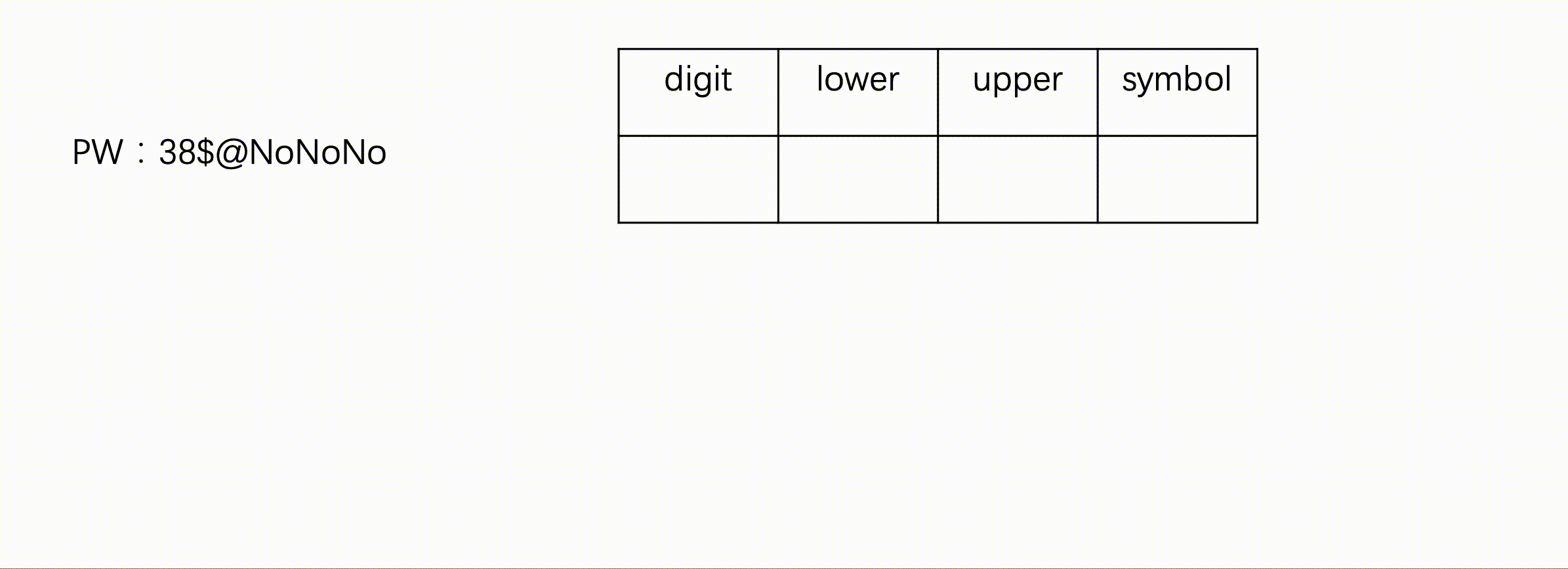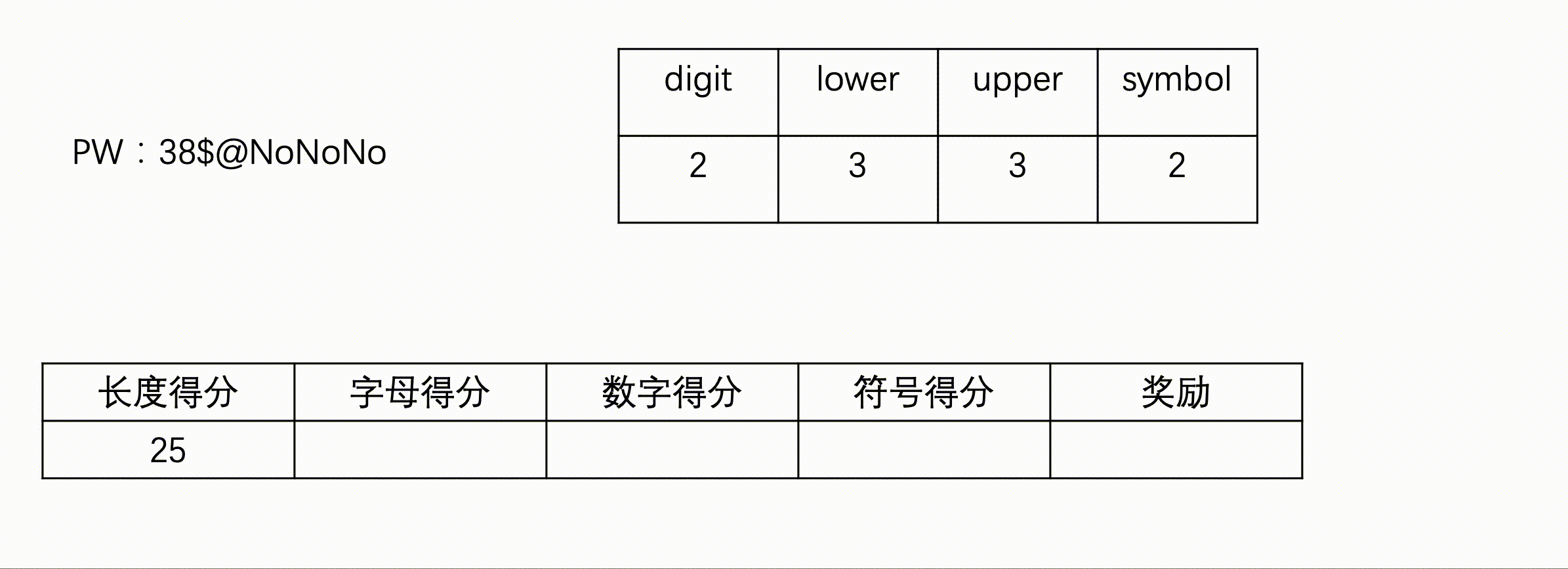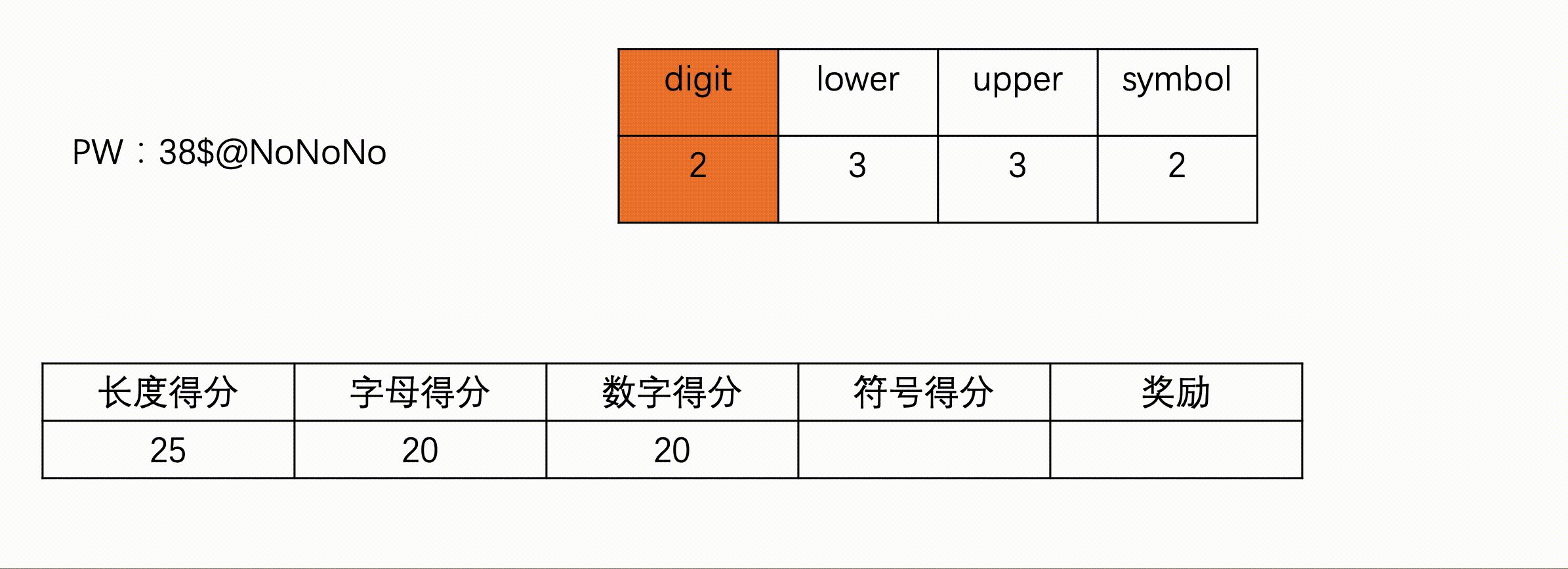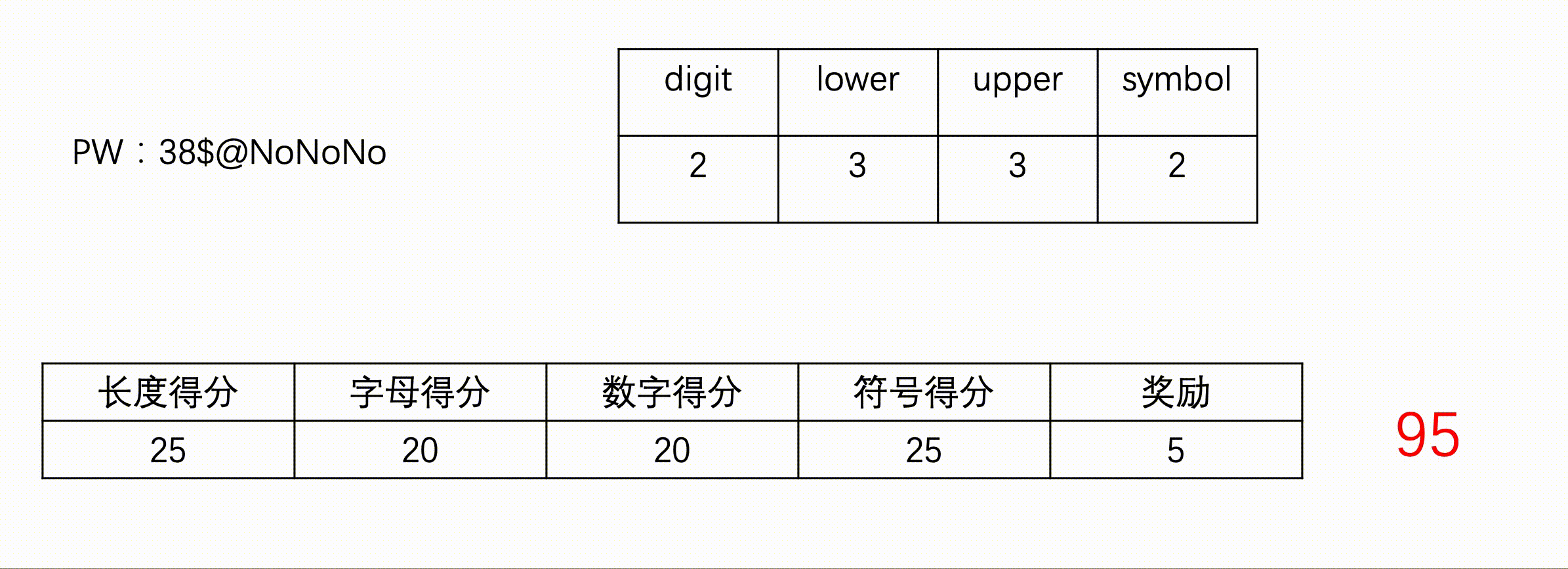
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin,s)){
int score=0;//分数
//密码长度
if(s.size()<=4){
score+=5;
}else if(s.size()>=8){
score+=25;
}else{
score+=10;
}
//字母 数字 符号个数
int lower=0,upper=0,digit=0,symbol=0,judge_zm=0,judge_fh=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(islower(s[i])){//小写字母
lower++;
}else if(isupper(s[i])){//大写字母
upper++;
}else if(isdigit(s[i])){//数字
digit++;
}else{//符号
symbol++;
}
}
//字母
if((lower >0 && upper==0)||(lower ==0 && upper>0)){//全都是小(大)写字母
score+=10;
}else if(lower>0 && upper>0){//大小写混合字母
score+=20;
}
//数字
if(digit==1){//1个数字
score+=10;
}else if(digit>1){//大于1个数字
score+=20;
}
//符号
if(symbol==1){//1个符号
score+=10;
}else if(symbol>1){//大于1个符号
score+=25;
}
//奖励
if(lower>0 && upper>0 && digit>0 && symbol>0){//大小写字母、数字、符号
score+=5;
}else if((lower>0||upper>0) && (digit>0) && (symbol>0)){//字母、数字、符号
score+=3;
}else if((lower>0||upper>0) && (digit>0)){//字母和数字
score+=2;
}
if(score>=90){
cout<<"VERY_SECURE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=80){
cout<<"SECURE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=70){
cout<<"VERY_STRONG"<<endl;
}else if(score>=60){
cout<<"STRONG"<<endl;
}else if(score>=50){
cout<<"AVERAGE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=25){
cout<<"WEAK"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"VERY_WEAK"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
方法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class PW{
private:
string password;
int upper = 0;
int lower = 0;
int digit = 0;
int symbol = 0;
public:
void init(string s){
this->password = s;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){ //统计大小写字母、数字、符号出现的次数
if(islower(s[i])){//小写字母
this->lower++;
}else if(isupper(s[i])){//大写字母
this->upper++;
}else if(isdigit(s[i])){//数字
this->digit++;
}else{//符号
this->symbol++;
}
}
}
int scoreOfLen(){ //计算长度得分
if(this->password.size() <= 4)
return 5;
else if(this->password.size() <= 7)
return 10;
return 25;
}
int scoreOfAlpha(){//计算字母得分
if(this->upper == 0 || this->lower == 0){
return 10;
}
else if(this->upper > 0 && this->lower > 0){
return 20;
}
return 0;
}
int scoreOfDigit(){//计算数字得分
if(this->digit == 1)
return 10;
else if(this->digit > 1)
return 20;
return 0;
}
int scoreOfSymbol(){//计算符号得分
if(this->symbol == 1){
return 10;
}
else if(this->symbol > 1){
return 25;
}
return 0;
}
int award(){//计算奖励分数
if(this->upper > 0 && this->lower > 0 && this->digit > 0 && this->symbol > 0)//同时有大小写字母、数字、符号
return 5;
else if(this->upper + this->lower > 0 && this->digit > 0 && this->symbol > 0)//有字母、数字、符号
return 3;
else if(this->upper + this->lower > 0 && this->digit > 0)//有字母、数字
return 2;
return 0;
}
};
int main(){
string s;
while(cin >> s){
PW str;
str.init(s);
int score = str.award() + str.scoreOfLen() + str.scoreOfAlpha() + str.scoreOfDigit() + str.scoreOfSymbol();//计算总分
//按照分数输出对应的密码强度等级
if(score>=90){
cout<<"VERY_SECURE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=80){
cout<<"SECURE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=70){
cout<<"VERY_STRONG"<<endl;
}else if(score>=60){
cout<<"STRONG"<<endl;
}else if(score>=50){
cout<<"AVERAGE"<<endl;
}else if(score>=25){
cout<<"WEAK"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"VERY_WEAK"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
HJ88 扑克牌大小
描述
扑克牌游戏大家应该都比较熟悉了,一副牌由54张组成,含3~A、2各4张,小王1张,大王1张。牌面从小到大用如下字符和字符串表示(其中,小写joker表示小王,大写JOKER表示大王):
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K A 2 joker JOKER
输入两手牌,两手牌之间用"-"连接,每手牌的每张牌以空格分隔,"-"两边没有空格,如:4 4 4 4-joker JOKER。
请比较两手牌大小,输出较大的牌,如果不存在比较关系则输出ERROR。
基本规则:
(1)输入每手牌可能是个子、对子、顺子(连续5张)、三个、炸弹(四个)和对王中的一种,不存在其他情况,由输入保证两手牌都是合法的,顺子已经从小到大排列;
(2)除了炸弹和对王可以和所有牌比较之外,其他类型的牌只能跟相同类型的存在比较关系(如,对子跟对子比较,三个跟三个比较),不考虑拆牌情况(如:将对子拆分成个子);
(3)大小规则跟大家平时了解的常见规则相同,个子、对子、三个比较牌面大小;顺子比较最小牌大小;炸弹大于前面所有的牌,炸弹之间比较牌面大小;对王是最大的牌;
(4)输入的两手牌不会出现相等的情况。
数据范围:字符串长度:3≤s≤10
输入描述:
输入两手牌,两手牌之间用"-"连接,每手牌的每张牌以空格分隔,"-"两边没有空格,如 4 4 4 4-joker JOKER。
输出描述:
输出两手牌中较大的那手,不含连接符,扑克牌顺序不变,仍以空格隔开;如果不存在比较关系则输出ERROR。
方法一:空格统计法
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int getvalue(string s){ //根据输入的字符首字母输出大小等级
switch(s[0]){
case '3': return 1;
case '4': return 2;
case '5': return 3;
case '6': return 4;
case '7': return 5;
case '8': return 6;
case '9': return 7;
case '1': return 8; //用1代替10
case 'J': return 9;
case 'Q': return 10;
case 'K': return 11;
case 'A': return 12;
case '2': return 13;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
string s1 = s.substr(0, s.find('-')); //从-处截取成两段
string s2 = s.substr(s.find('-') + 1);
int space1 = 0, space2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) //统计字符串中空格的数量
if(s1[i] == ' ')
space1++;
for(int i = 0; i < s2.length(); i++)
if(s2[i] == ' ')
space2++;
if(s1 == "joker JOKER" || s2 == "joker JOKER") //如果有王炸直接输出王炸
cout << "joker JOKER";
else if(space1 == 3 && space2 == 3){ //都有3个空格,说明4张牌,说明两个都是炸弹
if(getvalue(s1) > getvalue(s2)) //比较炸弹大小
cout << s1 << endl;
else
cout << s2 << endl;
}else if(space1 == 3) //字符串其中一个空格为3,说明一个是炸弹,输出炸弹
cout << s1 << endl;
else if(space2 == 3)
cout << s2 << endl;
else if(space1 == space2){ //没有炸弹的情况下相同类型才能比较
if(getvalue(s1) > getvalue(s2)) //个子、对子、三个、顺子都是比较第一个大小
cout << s1 << endl;
else
cout << s2 << endl;
}
else //无法比较
cout << "ERROR" << endl;
}
}
方法二:哈希表+长度比较法

#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//用哈希表记录每个字符相应的大小,其中10用字符1表示
unordered_map<char, int> nums{{'3', 1},{'4', 2}, {'5', 3}, {'6', 4}, {'7', 5},
{'8', 6}, {'9', 7}, {'1', 8},{'J', 9}, {'Q', 10}, {'K', 11}, {'A', 12}, {'2', 13}};
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
string s1_origin = s.substr(0, s.find('-')); //从-处截取成两段
string s2_origin = s.substr(s.find('-') + 1);
string s1 = "", s2 = "";
for(int i = 0; i < s1_origin.length(); i++) //将原字符串中的10变成1
if(s1_origin[i] != '0')
s1 += s1_origin[i];
for(int i = 0; i < s2_origin.length(); i++) //将原字符串中的10变成1
if(s2_origin[i] != '0')
s2 += s2_origin[i];
if(s1 == "joker JOKER" || s2 == "joker JOKER") //如果有王炸直接输出王炸
cout << "joker JOKER";
else if(s1.length() == 7 && s2.length() == 7){ //字符串长度都为7,说明两个都是炸弹
if(nums[s1[0]] > nums[s2[0]]) //比较炸弹大小
cout << s1_origin << endl;
else
cout << s2_origin << endl;
}else if(s1.length() == 7) //字符串其中一个为7,说明一个是炸弹,输出炸弹
cout << s1_origin << endl;
else if(s2.length() == 7)
cout << s2_origin << endl;
else if(s1.length() == s2.length()){ //没有炸弹的情况下相同类型才能比较
if(nums[s1[0]] > nums[s2[0]]) //个子、对子、三个、顺子都是比较第一个大小
cout << s1_origin << endl;
else
cout << s2_origin << endl;
}
else //无法比较
cout << "ERROR" << endl;
}
}
HJ89 24点运算
描述
计算24点是一种扑克牌益智游戏,随机抽出4张扑克牌,通过加(+),减(-),乘(*), 除(/)四种运算法则计算得到整数24,本问题中,扑克牌通过如下字符或者字符串表示,其中,小写joker表示小王,大写JOKER表示大王:
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K A 2 joker JOKER
本程序要求实现:输入4张牌,输出一个算式,算式的结果为24点。
详细说明:
1.运算只考虑加减乘除运算,没有阶乘等特殊运算符号,没有括号,友情提醒,整数除法要当心,是属于整除,比如2/3=0,3/2=1;
2.牌面210对应的权值为210, J、Q、K、A权值分别为为11、12、13、1;
3.输入4张牌为字符串形式,以一个空格隔开,首尾无空格;如果输入的4张牌中包含大小王,则输出字符串“ERROR”,表示无法运算;
4.输出的算式格式为4张牌通过+-*/四个运算符相连,中间无空格,4张牌出现顺序任意,只要结果正确;
5.输出算式的运算顺序从左至右,不包含括号,如1+2+34的结果为24,2 A 9 A不能变为(2+1)(9-1)=24
6.如果存在多种算式都能计算得出24,只需输出一种即可,如果无法得出24,则输出“NONE”表示无解。
7.因为都是扑克牌,不存在单个牌为0的情况,且没有括号运算,除数(即分母)的数字不可能为0
数据范围:一行由4张牌组成的字符串
输入描述:
输入4张牌为字符串形式,以一个空格隔开,首尾无空格;
输出描述:
输出怎么运算得到24,如果无法得出24,则输出“NONE”表示无解,如果输入的4张牌中包含大小王,则输出字符串“ERROR”,表示无法运算;
方法一:暴力枚举
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
unordered_map<string, int> CardtoNum = {{"A", 1}, {"2", 2}, {"3", 3}, {"4", 4}, {"5", 5}, {"6", 6},
{"7", 7}, {"8", 8}, {"9", 9}, {"10", 10}, {"J", 11}, {"Q", 12}, {"K", 13}}; //输入的字符映射到数字
unordered_map<int, string> NumtoCard = {{1, "A"}, {2, "2"}, {3, "3"}, {4, "4"}, {5, "5"}, {6, "6"},
{7, "7"}, {8, "8"}, {9, "9"}, {10, "10"}, {11, "J"}, {12, "Q"}, {13, "K"}}; //返回的数字映射到字符
const vector<char> Op = {'+', '-', '*', '/'}; //输出时符号映射
int cal(int a, int b, int op){ //运算
if(op == 0)
return a + b;
else if (op == 1)
return a - b;
else if (op == 2)
return a * b;
else
return a / b;
}
bool dfs(const vector<int>& nums, int start, int sum, int op, vector<int>& ops){ //查找这个数字顺序下有无合适的符号可以让结果等于24
int newSum = cal(sum, nums[start], op);
if(start == 3 && newSum == 24) //末尾比较是否到了24
return true;
else if (start == 3)
return false;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ //遍历所有情况的符号
ops.push_back(i); //尝试每个符号
if (dfs(nums, start + 1, newSum, i, ops)) //递归计算
return true;
ops.pop_back(); //回溯
}
return false;
}
int main() {
vector<string> s(4);
cin >> s[0] >> s[1] >> s[2] >> s[3]; //输入4个字符串
vector<int> nums(4);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if(s[i] == "joker" || s[i] == "JOKER"){ //遇到大小王
cout << "ERROR" << endl;
return 0;
}
nums[i] = CardtoNum[s[i]]; //字符串转数字
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); //排成递增序
do {
vector<int> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ //遍历开头四种运算符
ops.push_back(i);
if (dfs(nums, 1, nums[0], i, ops)){ //递归计算这个顺序的顺子有无运算符可以完成
cout << NumtoCard[nums[0]] << Op[ops[0]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[1]] << Op[ops[1]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[2]] << Op[ops[2]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[3]] << endl;
return 0;
}
ops.pop_back(); //回溯
}
} while(next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())); //枚举所有的顺序
cout << "NONE" << endl;
return 0;
}
方法二:枚举+递归
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
unordered_map<string, int> CardtoNum = {{"A", 1}, {"2", 2}, {"3", 3}, {"4", 4}, {"5", 5}, {"6", 6},
{"7", 7}, {"8", 8}, {"9", 9}, {"10", 10}, {"J", 11}, {"Q", 12}, {"K", 13}}; //输入的字符映射到数字
unordered_map<int, string> NumtoCard = {{1, "A"}, {2, "2"}, {3, "3"}, {4, "4"}, {5, "5"}, {6, "6"},
{7, "7"}, {8, "8"}, {9, "9"}, {10, "10"}, {11, "J"}, {12, "Q"}, {13, "K"}}; //返回的数字映射到字符
const vector<char> Op = {'+', '-', '*', '/'}; //输出时符号映射
int cal(int a, int b, int op){ //运算
if(op == 0)
return a + b;
else if (op == 1)
return a - b;
else if (op == 2)
return a * b;
else
return a / b;
}
bool dfs(const vector<int>& nums, int start, int sum, int op, vector<int>& ops){ //查找这个数字顺序下有无合适的符号可以让结果等于24
int newSum = cal(sum, nums[start], op);
if(start == 3 && newSum == 24) //末尾比较是否到了24
return true;
else if (start == 3)
return false;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ //遍历所有情况的符号
ops.push_back(i); //尝试每个符号
if (dfs(nums, start + 1, newSum, i, ops)) //递归计算
return true;
ops.pop_back(); //回溯
}
return false;
}
int main() {
vector<string> s(4);
cin >> s[0] >> s[1] >> s[2] >> s[3]; //输入4个字符串
vector<int> nums(4);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if(s[i] == "joker" || s[i] == "JOKER"){ //遇到大小王
cout << "ERROR" << endl;
return 0;
}
nums[i] = CardtoNum[s[i]]; //字符串转数字
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); //排成递增序
do {
vector<int> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ //遍历开头四种运算符
ops.push_back(i);
if (dfs(nums, 1, nums[0], i, ops)){ //递归计算这个顺序的顺子有无运算符可以完成
cout << NumtoCard[nums[0]] << Op[ops[0]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[1]] << Op[ops[1]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[2]] << Op[ops[2]]
<< NumtoCard[nums[3]] << endl;
return 0;
}
ops.pop_back(); //回溯
}
} while(next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())); //枚举所有的顺序
cout << "NONE" << endl;
return 0;
}
HJ90 合法IP
描述
IPV4地址可以用一个32位无符号整数来表示,一般用点分方式来显示,点将IP地址分成4个部分,每个部分为8位,表示成一个无符号整数(因此正号不需要出现),如10.137.17.1,是我们非常熟悉的IP地址,一个IP地址串中没有空格出现(因为要表示成一个32数字)。
现在需要你用程序来判断IP是否合法。
数据范围:数据组数:1≤t≤18
进阶:时间复杂度:O(n) ,空间复杂度:O(n)
输入描述:
输入一个ip地址,保证不包含空格
输出描述:
返回判断的结果YES or NO
方法一:字符串流输入输出

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string ip;
while(getline(cin, ip)){
stringstream ss;
ss << ip;
unsigned a, b, c, d;
char c1, c2, c3; //接收点
ss >> a >> c1 >> b >> c2 >> c >> c3 >> d; //流输出数组和字符
//判断数字范围
if(a >= 0 && a <= 255 && b >= 0 && b <= 255 && c >= 0 && c <= 255 && d >= 0 && d <= 255)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:正则表达式
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<regex>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string ip;
regex pattern("((25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|1\\d\\d|[1-9]\\d|\\d)\.){4}");//匹配0.0.0.0.-255.255.255.255.的正则表达式
while(getline(cin, ip)){
ip += "."; //正则表达式匹配的四个点,ip地址后面再加一个
if(regex_match(ip, pattern)) //匹配函数
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}




